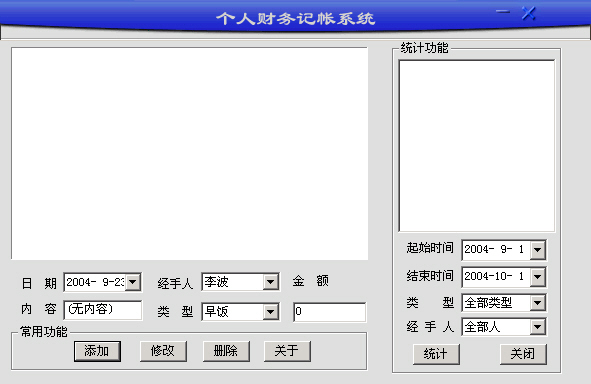
这是我改写的一个个人财务记帐系统,其主要功能是将个人每天的财务状况记录到数据库,并有统计功能。
这个程序主要采用目前比较流行的ADO技术,考虑到程序的小巧和方便,存取采用ACCESS数据库实现。
核心代码实现如下:
(1)、引入ADO类
#import “c:\program files\common files\system\ado\msado15.dll”
no_namespace
rename (“EOF”, “adoEOF”)
(2)、初始化COM
在MFC中可以用AfxOleInit();非MFC环境中用: CoInitialize(NULL);
CoUnInitialize();
(3)#import 包含后就可以用3个智能指针了:_ConnectionPtr、_RecordsetPtr和_CommandPtr
1.连接和关闭数据库 (1)连接
例子:连接Access数据库
m_pConnection.CreateInstance(__uuidof(Connection));
try
{
// 打开本地Access库Demo.mdb
m_pConnection->Open(“Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;DataSource=Demo.mdb”,
“”,””,adModeUnknown);
}
catch(_com_error e)
{
AfxMessageBox(“数据库连接失败,确认数据库Demo.mdb是否在当前路径下!”);
return FALSE;
}
(2)、关闭
//如果数据库连接有效
if(m_pConnection->State)
m_pConnection->Close();
m_pConnection= NULL;
(3)、设置连接时间 //设置连接时间———————————– pConnection->put_ConnectionTimeout(long(5));
2.打开一个结果集
(1)打开,首先创建一个_RecordsetPtr实例,然后调用Open()得到一条SQL语句的执行结果
_RecordsetPtr m_pRecordset;
m_pRecordset.CreateInstance(__uuidof(Recordset));
// 在ADO操作中建议语句中要常用try…catch()来捕获错误信息,
// 因为它有时会经常出现一些意想不到的错误。jingzhou xu
try
{
m_pRecordset->Open(“SELECT * FROM DemoTable”,// 查询DemoTable表中所有字段
m_pConnection.GetInterfacePtr(), // 获取库接库的IDispatch指针
adOpenDynamic,
adLockOptimistic,
adCmdText);
}
catch(_com_error *e)
{
AfxMessageBox(e->ErrorMessage());
}
(2)关闭结果集 m_pRecordset->Close();
3.操作一个结果集
(1)、遍历(读取)
a)、用pRecordset->adoEOF来判断数据库指针是否已经移到结果集的末尾了;m_pRecordset->BOF判断是否 在第一条记录前面: while(!m_pRecordset->adoEOF)
{
var = m_pRecordset->GetCollect(“Name”);
if(var.vt != VT_NULL)
strName = (LPCSTR)_bstr_t(var);
var = m_pRecordset->GetCollect(“Age”);
if(var.vt != VT_NULL)
strAge = (LPCSTR)_bstr_t(var);
m_AccessList.AddString( strName + “ –> “+strAge );
m_pRecordset->MoveNext();
}
b)、取得一个字段的值的办法有两种办法
一是
//表示取得第0个字段的值 m_pRecordset->GetCollect(“Name”);
或者 m_pRecordset->GetCollect(_variant_t(long(0));
二是
pRecordset->get_Collect(“COLUMN_NAME”);
或者 pRecordset->get_Collect(long(index));
(2)、添加
a)、调用m_pRecordset->AddNew();
b)、调用m_pRecordset->PutCollect();给每个字段赋值
c)、调用m_pRecordset->Update();确认
(3)、修改
(4)、删除
a)、把记录指针移动到要删除的记录上,然后调用Delete(adAffectCurrent) try
{
// 假设删除第二条记录
m_pRecordset->MoveFirst();
m_pRecordset->Move(1);
// 从0开始
m_pRecordset->Delete(adAffectCurrent);
// 参数adAffectCurrent为删除当前记录
m_pRecordset->Update();
}
catch(_com_error *e)
{
AfxMessageBox(e->ErrorMessage());
}
4.直接执行SQL语句,除了要用到结果集其余的大部分功能都可以直接用SQL语言实现
(1)、用_CommandPtr和_RecordsetPtr配合
_CommandPtr m_pCommand;
m_pCommand.CreateInstance(__uuidof(Command));
// 将库连接赋于它
m_pCommand->ActiveConnection = m_pConnection;
// SQL语句
m_pCommand->CommandText = “SELECT * FROM DemoTable”;
// 执行SQL语句,返回记录集
m_pRecordset = m_pCommand->Execute(NULL, NULL,adCmdText);
(2)、直接用_ConnectionPtr执行SQL语句
_RecordsetPtr Connection15::Execute ( _bstr_t CommandText,
VARIANT * RecordsAffected,
long Options )
其中CommandText是命令字串,通常是SQL命令。
参数RecordsAffected是操作完成后所影响的行数,
参数Options表示CommandText中内容的类型,Options可以取如下值之一:
adCmdText:表明CommandText是文本命令
adCmdTable:表明CommandText是一个表名
adCmdProc:表明CommandText是一个存储过程
adCmdUnknown:未知
例子:
_variant_t RecordsAffected;
m_pConnection->Execute(“UPDATE users SET old = old+1”,&RecordsAffected;,adCmdText);
5.调用存储过程
(1)、利用_CommandPtr
_CommandPtr m_pCommand;
m_pCommand.CreateInstance(__uuidof(Command));
m_pCommand->ActiveConnection = m_pConnection; // 将库连接赋于它
m_pCommand->CommandText = “Demo”;
m_pCommand->Execute(NULL,NULL, adCmdStoredProc);
(2)、直接用_ConnectionPtr直接调用(见4.(2))
6.遍历数据库中的所有表名 _ConnectionPtr m_pConnect;
_RecordsetPtr pSet;
HRESULT hr;
try
{
hr = m_pConnect.CreateInstance(“ADODB.Connection”);
if(SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
CString dd;
dd.Format(“Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=%s”,file);
hr = m_pConnect->Open((_bstr_t)dd,””,””,adModeUnknown);
pSet = m_pConnect->OpenSchema(adSchemaTables);
while(!(pSet->adoEOF))
{
//获取表格
_bstr_t table_name = pSet->Fields->GetItem(“TABLE_NAME”)->Value;
//获取表格类型
_bstr_t table_type = pSet->Fields->GetItem("TABLE_TYPE")->Value;
//过滤一下,只输出表格名称,其他的省略
if ( strcmp(((LPCSTR)table_type),"TABLE")==0){
CString tt;
tt.Format("%s",(LPCSTR)table_name);
AfxMessageBox(tt);
}
pSet->MoveNext();
}
pSet->Close();
}
m_pConnect->Close();
}catch(_com_error e)///捕捉异常
{
CString errormessage;
errormessage.Format(“连接数据库失败!rn错误信息:%s”,e.ErrorMessage());
AfxMessageBox(errormessage);
return -1;
}
7.遍历一个表中的所有字段
Field * field = NULL;
HRESULT hr;
Fields * fields = NULL;
hr = m_pRecordset->get_Fields (&fields;); //得到记录集的字段集和
if(SUCCEEDED(hr))
fields->get_Count(&ColCount;);
//得到记录集的字段集合中的字段的总个数
for(i=0;iItem[i]->get_Name(&bstrColName;); //得到记录集//中的字段名
strColName=bstrColName;
nameField = strColName;
m_FieldsList.AddString(nameField);
}
if(SUCCEEDED(hr))
fields->Release();//释放指针
附:
1、_variant_t
(1)、一般传给这3个指针的值都不是MFC直接支持的数据类型,而要用_variant_t转换一下
_variant_t(XX)可以把大多数类型的变量转换成适合的类型传入:
(2)、_variant_t var;_variant_t -> long: (long)var;
_variant_t -> CString: CString strValue = (LPCSTR)_bstr_t(var);
CString -> _variant_t: _variant_t(strSql);
2、BSTR宽字符串与CString相互转换
BSTR bstr;
CString strSql;
CString -> BSTR: bstr = strSql.AllocSysString();
BSTR -> CString: strSql = (LPCSTR)bstr;
3、_bstr_t与CString相互转换
_bstr_t bstr;
CString strSql;
CString -> _bstr_t: bstr = (_bstr_t)strSql;
_bstr_t -> CString: strSql = (LPCSTR)bstr;
4、关于时间
Access:表示时间的字符串#2004-4-5#
Sql:表示时间的字符串’’2004-4-5’’
DateField(时间字段) select * from my_table where DateField > #2004-4-10#
源代码下载:
点击下载此文件
应用程序下载:
点击下载此文件